Two common injuries suffered in car wrecks are whiplash and concussion. Though both of these injuries can have lasting and significant impacts on a person’s life, they can be entirely different or they may be part of the total injury presentation. It is important to understand the distinction between them and the reasons that the two injuries may co-exist making for a doubly unhappy patient. There have been many occasions where a new client interview has uncovered concussion symptoms previously thought to be related to a cervical whiplash. Please continue reading and reach out to a seasoned Stamford, Connecticut auto accident lawyer from Casper & de Toledo to learn more about the differences between whiplash and a concussion and how our firm can help fight for the compensation you deserve. Here are some of the questions you may have:
How is whiplash different from a concussion?
To start, you should understand that whiplash is a neck injury, while a concussion is a head injury. Whiplash occurs when the neck forcefully moves back and forth, which often happens in auto accidents. Whiplash is more technically known as an acceleration-deceleration injury. Some of the most common symptoms of whiplash include neck pain, fatigue, tingling or numbness in the arms that sometimes radiates to the fingers, tenderness in the shoulder or upper back, headache, worsening of pain with neck movement, and more. Symptoms that radiate into the arms, including weakness, are signs of nerve root irritation and/or possible cervical disk damage or irritation.
Though a concussion is a different injury, some symptoms of concussions can be similar to those of whiplash, such as headaches and fatigue. That said, there are various other symptoms that are more exclusive to concussions, including ringing in the ears, nausea, dizziness, personality changes, mood swings, and vomiting.
Logically, because brain injury is often the result of linear and rotational movement of the brain inside the hard vault of the skull – it is easy to understand that the mechanism of “whiplash” can also cause a concussive brain injury.
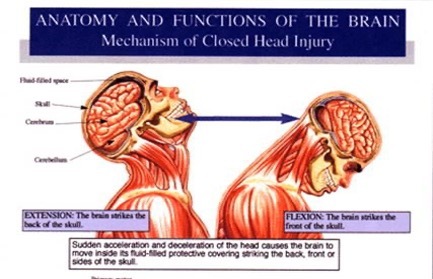
In addition, it is not necessary to strike the head in a crash or a fall to sustain a concussion because the mechanism of injury can be the same. So it is common for a patient diagnosed with a concussion to also experience “whiplash” and anecdotally, it is common for a patient suffering “whiplash”, to experience similar symptoms. Those similar symptoms might be part and parcel of the whiplash but might also be part of an undiagnosed concussion or sub-concussive event.
How can you determine whether the injury is to the neck, the brain, or both? Well, a diagnosis must be made by a qualified healthcare provider. As lawyers, there are certain factors that raise our index of suspicion. First is the most obvious – you come to us with a diagnosis of concussion. That early diagnosis may have been made in the Emergency Room (ER). A concussion diagnosis is often missed in the ER because the staff is primarily interested in ruling out life-threatening conditions. This can also occur because the focus on you, the patient, may be on other more obvious injuries such as a fracture. The second factor we generally consider is the duration of the symptoms. If an accident occurred less than 90 days prior to the consultation, the potential new client is still within the window of spontaneous recovery from concussion. At the earliest stage of the initial 90 days, the patient can be patient and follow the general recommendations to rest, avoid screen time, and avoid activities that make the symptoms worse. As the end of that initial 90-day window approaches, if the symptoms are trending toward recovery, that is encouraging. If the symptoms remain or plateau, that is more concerning and may warrant suggestions to redirect some of the health care evaluations to professionals who focus on concussion and TBI. The important point to understand is that the diagnosis of a concussion or mild traumatic brain injury can be confusing or be missed by well-intentioned but unsophisticated healthcare providers. It is important that you understand that your symptoms, whatever they are, should be taken seriously and followed until you begin to improve.
What should I do if I think I have whiplash or a concussion?
After an auto accident, the most important thing you can do is seek immediate medical treatment, regardless of whether you feel any symptoms. Many injuries can take hours, days, or even weeks to set in and present themselves, so it’s important you are proactive and get checked out at once. If you believe you have whiplash or a concussion or perhaps both, it’s important to be open and honest with your doctor. Inform them of all of your symptoms to ensure you receive the proper testing and treatment.
Should I hire a lawyer?
If you sustained whiplash, a concussion, or any other type of injury in an auto accident caused by another negligent driver, you should absolutely hire an attorney, as you likely will have a viable path to compensation. As long as we can satisfy the burden of proof in your personal injury claim, you should receive compensation to help you recuperate from the economic and non-economic damages you’ve incurred as a result of your accident.

